Managed Spot Jobs
Contents
Managed Spot Jobs¶
SkyPilot supports managed spot jobs that can automatically recover from preemptions. This feature saves significant cost (e.g., up to 70% for GPU VMs) by making preemptible spot instances practical for long-running jobs.
SkyPilot automatically finds available spot resources across regions and clouds to maximize availability. Here is an example of a BERT training job failing over different regions across AWS and GCP.
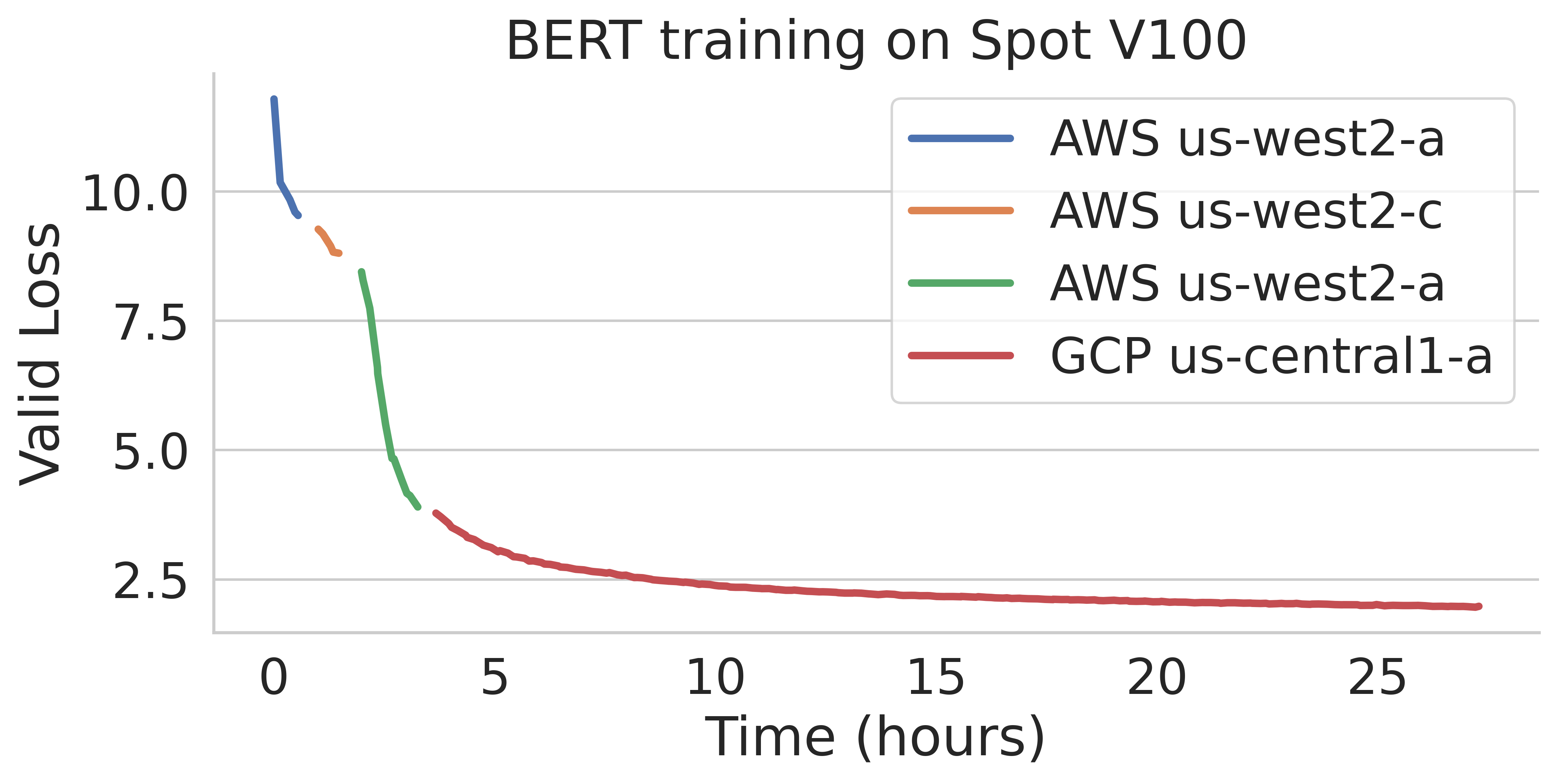
Below are the requirements for using managed spot jobs:
Task YAML: Managed Spot requires a YAML to describe the job, tested with
sky launch.Checkpointing and recovery (optional): For job recovery with less progress resuming, application code can checkpoint periodically to a SkyPilot Storage-mounted cloud bucket. The program can reload the latest checkpoint when restarted.
Task YAML¶
To launch a spot job, you can simply reuse your task YAML (recommended to test it with sky launch first).
For example, we found the BERT fine-tuning YAML works with sky launch, and want to
launch it with SkyPilot managed spot jobs.
We can launch it with the following:
$ sky spot launch -n bert-qa bert_qa.yaml
# bert_qa.yaml
name: bert_qa
resources:
accelerators: V100:1
# Assume your working directory is under `~/transformers`.
# To make this example work, please run the following command:
# git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git ~/transformers -b v4.18.0
workdir: ~/transformers
setup: |
# Fill in your wandb key: copy from https://wandb.ai/authorize
# Alternatively, you can use `--env WANDB_API_KEY=$WANDB_API_KEY`
# to pass the key in the command line, during `sky spot launch`.
echo export WANDB_API_KEY=[YOUR-WANDB-API-KEY] >> ~/.bashrc
pip install -e .
cd examples/pytorch/question-answering/
pip install -r requirements.txt torch==1.12.1+cu113 --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113
pip install wandb
run: |
cd ./examples/pytorch/question-answering/
python run_qa.py \
--model_name_or_path bert-base-uncased \
--dataset_name squad \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--per_device_train_batch_size 12 \
--learning_rate 3e-5 \
--num_train_epochs 50 \
--max_seq_length 384 \
--doc_stride 128 \
--report_to wandb
Note
workdir and file mounts with local files will be automatically uploaded to SkyPilot Storage. Cloud bucket will be created during the job running time, and cleaned up after the job finishes.
SkyPilot will launch and start monitoring the spot job. When a preemption happens, SkyPilot will automatically search for resources across regions and clouds to re-launch the job.
In this example, the job will be restarted from scratch after each preemption recovery. To resume the job from previous states, user’s application needs to implement checkpointing and recovery.
Checkpointing and recovery¶
To allow spot recovery, a cloud bucket is typically needed to store the job’s states (e.g., model checkpoints).
Below is an example of mounting a bucket to /checkpoint.
file_mounts:
/checkpoint:
name: # NOTE: Fill in your bucket name
mode: MOUNT
The MOUNT mode in SkyPilot Storage ensures the checkpoints outputted to /checkpoint are automatically synced to a persistent bucket.
Note that the application code should save program checkpoints periodically and reload those states when the job is restarted.
This is typically achieved by reloading the latest checkpoint at the beginning of your program.
An end-to-end example¶
Below we show an example for fine-tuning a BERT model on a question-answering task with HuggingFace.
# bert_qa.yaml
name: bert_qa
resources:
accelerators: V100:1
# Assume your working directory is under `~/transformers`.
# To make this example work, please run the following command:
# git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git ~/transformers -b v4.18.0
workdir: ~/transformers
file_mounts:
/checkpoint:
name: # NOTE: Fill in your bucket name
mode: MOUNT
setup: |
# Fill in your wandb key: copy from https://wandb.ai/authorize
# Alternatively, you can use `--env WANDB_API_KEY=$WANDB_API_KEY`
# to pass the key in the command line, during `sky spot launch`.
echo export WANDB_API_KEY=[YOUR-WANDB-API-KEY] >> ~/.bashrc
pip install -e .
cd examples/pytorch/question-answering/
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install wandb
run: |
cd ./examples/pytorch/question-answering/
python run_qa.py \
--model_name_or_path bert-base-uncased \
--dataset_name squad \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--per_device_train_batch_size 12 \
--learning_rate 3e-5 \
--num_train_epochs 50 \
--max_seq_length 384 \
--doc_stride 128 \
--report_to wandb \
--run_name $SKYPILOT_JOB_ID \
--output_dir /checkpoint/bert_qa/ \
--save_total_limit 10 \
--save_steps 1000
As HuggingFace has built-in support for periodically checkpointing, we only need to pass the highlighted arguments for setting up the output directory and frequency of checkpointing (see more on Huggingface API). You may also refer to another example here for periodically checkpointing with PyTorch.
We also set --run_name to $SKYPILOT_JOB_ID so that the loggings will be saved
to the same run in Weights & Biases.
Note
The environment variable $SKYPILOT_JOB_ID (example: “sky-2022-10-06-05-17-09-750781_spot_id-22”) can be used to identify the same job, i.e., it is kept identical across all
recoveries of the job.
It can be accessed in the task’s run commands or directly in the program itself (e.g., access
via os.environ and pass to Weights & Biases for tracking purposes in your training script). It is made available to
the task whenever it is invoked.
With the highlighted changes, the managed spot job can now resume training after preemption with sky spot launch! We can enjoy the benefits of
cost savings from spot instances without worrying about preemption or losing progress.
$ sky spot launch -n bert-qa bert_qa.yaml
Useful CLIs¶
Here are some commands for managed spot jobs. Check sky spot --help for more details.
# Check the status of the spot jobs
$ sky spot queue
Fetching managed spot job statuses...
Managed spot jobs:
ID NAME RESOURCES SUBMITTED TOT. DURATION JOB DURATION #RECOVERIES STATUS
2 roberta 1x [A100:8] 2 hrs ago 2h 47m 18s 2h 36m 18s 0 RUNNING
1 bert-qa 1x [V100:1] 4 hrs ago 4h 24m 26s 4h 17m 54s 0 RUNNING
# Stream the logs of a running spot job
$ sky spot logs -n bert-qa
# Cancel a spot job by name
$ sky spot cancel -n bert-qa
Spot controller (Advanced)¶
There will be a single spot controller VM (a small on-demand CPU VM) running in the background to manage all the spot jobs.
It will be autostopped after all spot jobs finished and no new spot job is submitted for 10 minutes. Typically no user intervention is needed.
You can find the controller with sky status, and refresh the status with sky status -r.
Although, the cost of the spot controller is negligible (~$0.4/hour when running and less than $0.004/hour when stopped),
you can still tear it down manually with
sky down <spot-controller-name>, where the <spot-controller-name> can be found in the output of sky status.
Note
Tearing down the spot controller will lose all logs and status information for the spot jobs and can cause resource leakage when there are still in-progress spot jobs.
